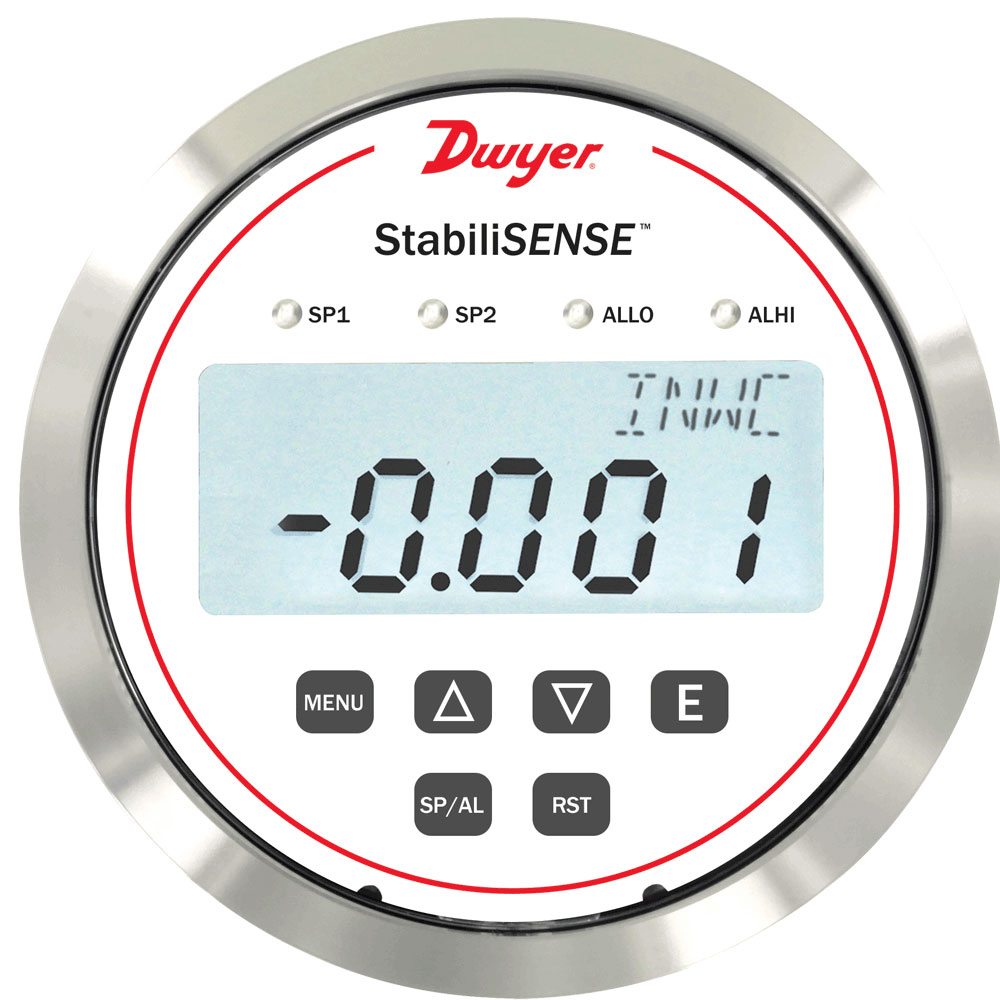
 Stability is defined as a change (or lack of change) in accuracy over a period of time.
Stability is defined as a change (or lack of change) in accuracy over a period of time.
Drift is commonly used as a specification to illustrate the stability, or change in accuracy over a period of time, commonly shown as X%/year where X = a number; i.e. 0.25%/year. In this scenario, a device with a ±1% accuracy, would be expected to have an accuracy of ±1.25% (1%+0.25%) after a period of one year. Depending on the design, brand, and range of the sensing instrument, the stability can vary widely. Continue reading “What is Stability and Why is it Important?”
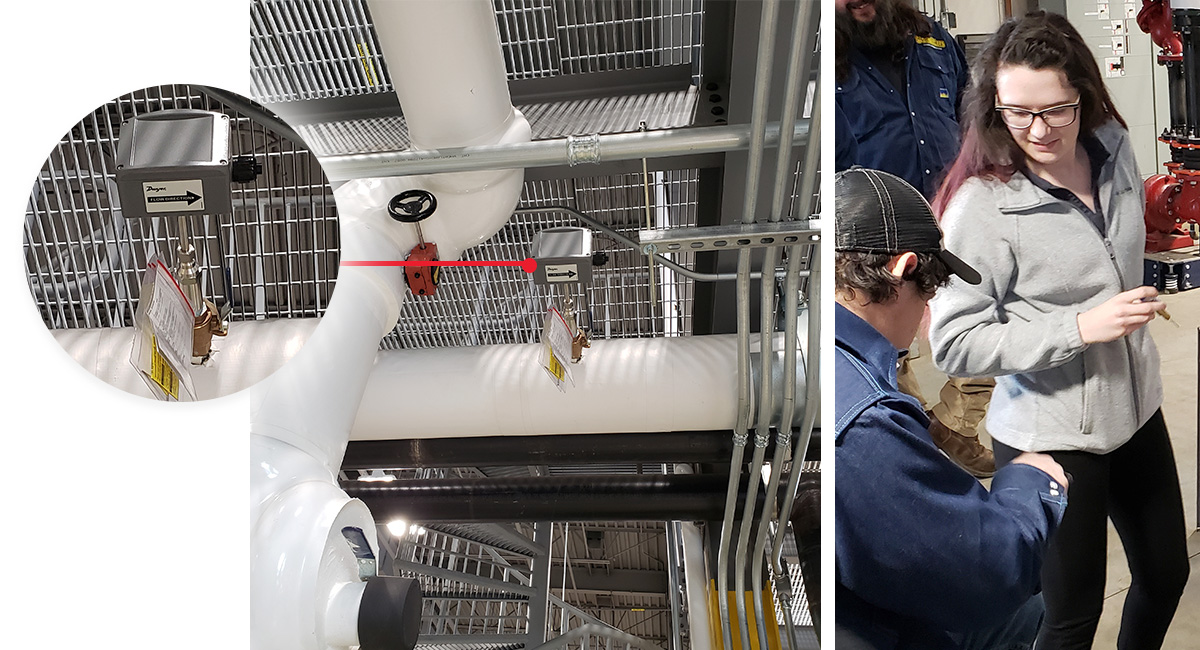




 The
The 
 Dwyer’s Account Executive for our test equipment portfolio, Jaden Lane, recently interviewed Erik from Technical Balance to learn more about his job, company, and relationship with Dwyer.
Dwyer’s Account Executive for our test equipment portfolio, Jaden Lane, recently interviewed Erik from Technical Balance to learn more about his job, company, and relationship with Dwyer. 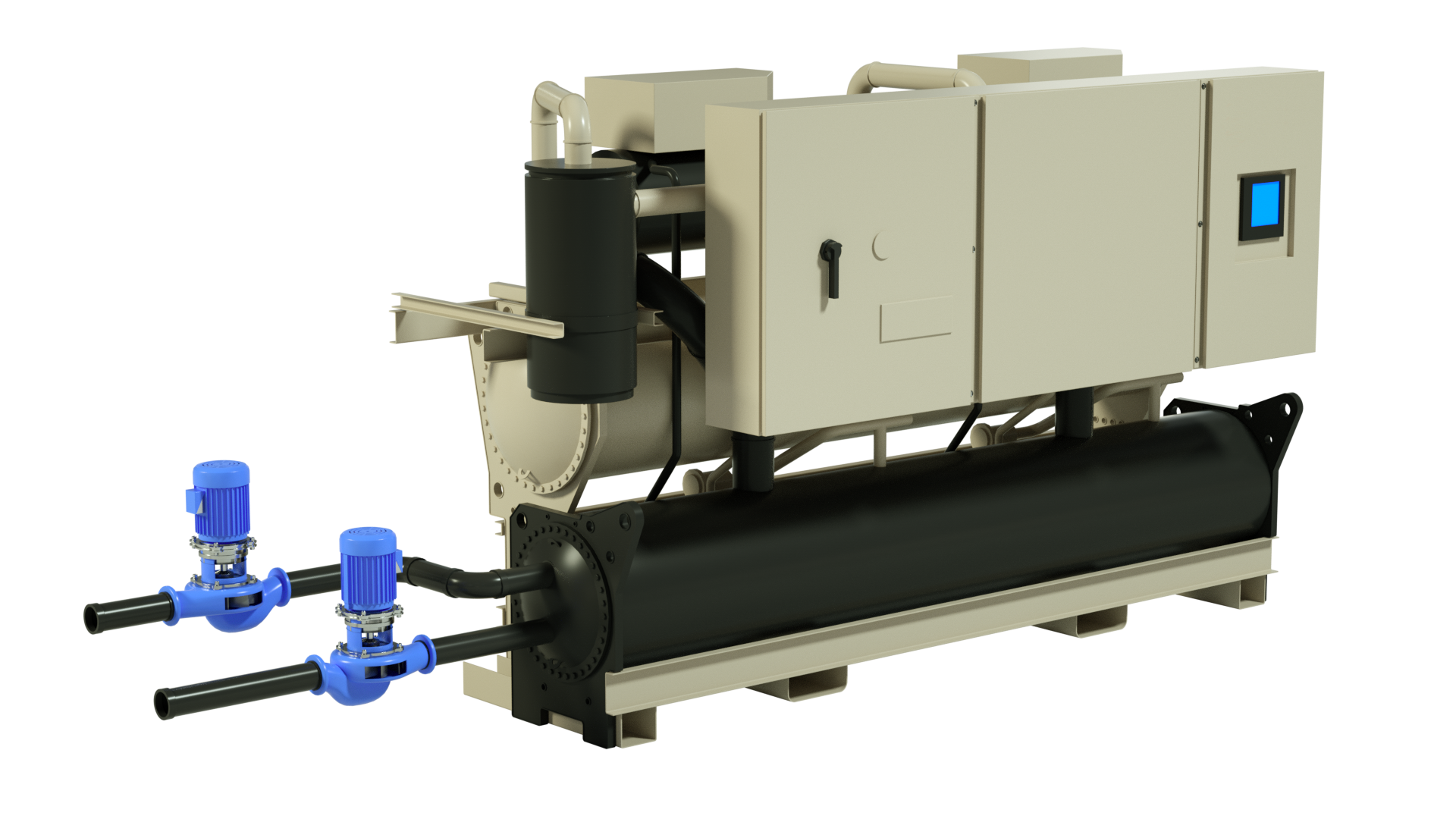
 Water chillers are nothing new, with nearly an estimated 100,000 units operating in North America alone. Chillers are the cooling machines of choice to condition industrial, commercial, and institutional facilities. They are used to lower the temperatures of all kinds of equipment and processes such as: robotic machinery; semiconductors; injection and blow molding machines; welding equipment; die-casting and machine tooling; paper and cement processing; power supplies; power generation stations; compressed air and gas cooling systems; medical imaging machines; chemical, drug, food and beverage production; even simply to cool potable water to desirable levels. Whether for office comfort, keeping data server centers from overheating, or specialized industrial processes, water temperature control plays a vital role in many of the behind-the-scenes activities that affect our everyday lives.
Water chillers are nothing new, with nearly an estimated 100,000 units operating in North America alone. Chillers are the cooling machines of choice to condition industrial, commercial, and institutional facilities. They are used to lower the temperatures of all kinds of equipment and processes such as: robotic machinery; semiconductors; injection and blow molding machines; welding equipment; die-casting and machine tooling; paper and cement processing; power supplies; power generation stations; compressed air and gas cooling systems; medical imaging machines; chemical, drug, food and beverage production; even simply to cool potable water to desirable levels. Whether for office comfort, keeping data server centers from overheating, or specialized industrial processes, water temperature control plays a vital role in many of the behind-the-scenes activities that affect our everyday lives.