 Dwyer Instruments offers a multitude of sensors for monitoring air velocity in HVAC systems. Some of this instrumentation has a simple construction (Pitot tubes, for example) while others are more complex, such as hot-wire anemometers.
Dwyer Instruments offers a multitude of sensors for monitoring air velocity in HVAC systems. Some of this instrumentation has a simple construction (Pitot tubes, for example) while others are more complex, such as hot-wire anemometers.
The initial term and first “hot-wire anemometer” was developed back in 1914 by Louie Vesso King. He is also accredited for King’s Law, which mathematically describes heat transfer in air flows using a heated wire. As the air moves over the wire, it causes a loss of temperature in the wire and removes some of the wire’s heat energy. Continue reading “Understanding Air Velocity Sensors”



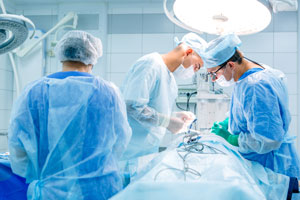
 Hot-wire anemometers are often used in a hospital environment to measure and maintain room pressurization/de-pressurization. These applications require a positive pressure in operating rooms where bacteria cannot be allowed to enter, or a negative pressure in a quarantine environment to ensure that all bacteria will stay within the room.
Hot-wire anemometers are often used in a hospital environment to measure and maintain room pressurization/de-pressurization. These applications require a positive pressure in operating rooms where bacteria cannot be allowed to enter, or a negative pressure in a quarantine environment to ensure that all bacteria will stay within the room. 