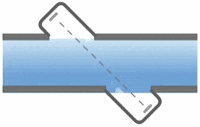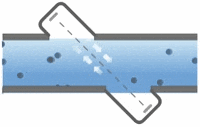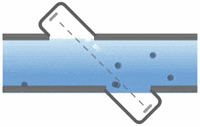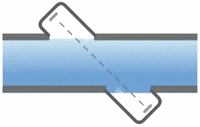
Electromagnetic flowmeters, also known as magnetic flowmeters or magmeters, use Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction to determine the flow of liquid in a pipe. In an electromagnetic flowmeter, a magnetic field is generated and channeled into the liquid flowing through the pipe. Following Faraday’s Law, flow of a conductive liquid through the magnetic field will cause a voltage signal to be sensed by electrodes located on the flow tube walls. When the fluid moves faster, more voltage is generated. Faraday’s Law states that the voltage generated is proportional to the movement of the flowing liquid. The electronic transmitter processes the voltage signal to determine liquid flow.
Electromagnetic flowmeters, also known as magnetic flowmeters or magmeters, use Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction to determine the flow of liquid in a pipe. In an electromagnetic flowmeter, a magnetic field is generated and channeled into the liquid flowing through the pipe. Following Faraday’s Law, flow of a conductive liquid through the magnetic field will cause a voltage signal to be sensed by electrodes located on the flow tube walls. When the fluid moves faster, more voltage is generated. Faraday’s Law states that the voltage generated is proportional to the movement of the flowing liquid. The electronic transmitter processes the voltage signal to determine liquid flow.
In contrast with many other flowmeter technologies, electromagnetic flowmeter technology produces signals that are linear with flow. As such, the turndown associated with magnetic flowmeters can approach 20:1 or better without sacrificing accuracy. Continue reading “How Electromagnetic Flowmeters Work”
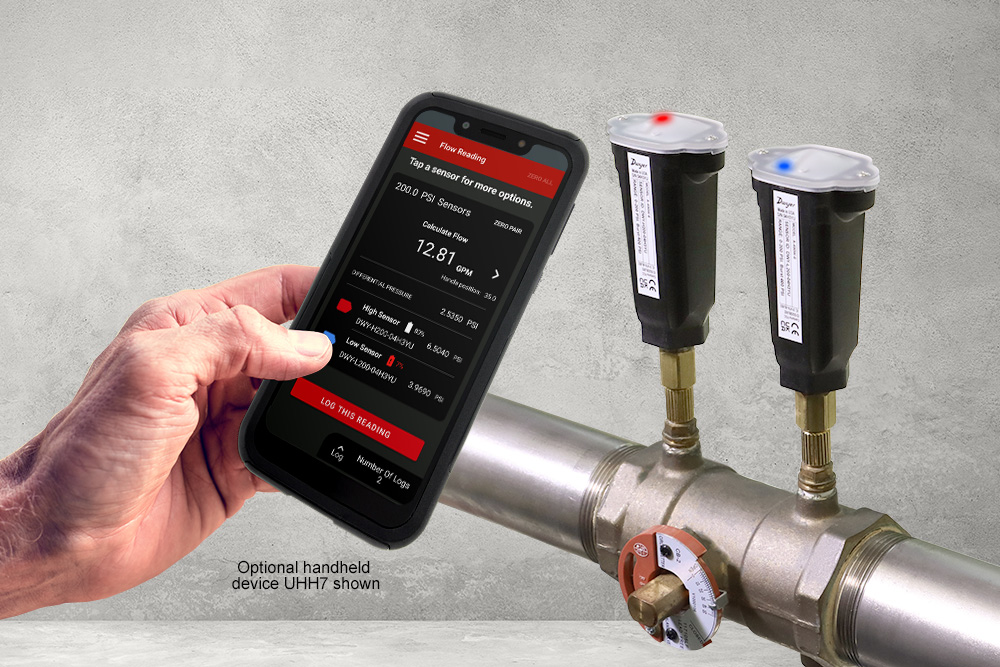




 Dwyer Instruments offers a multitude of sensors for monitoring air velocity in HVAC systems. Some of this instrumentation has a simple construction (Pitot tubes, for example) while others are more complex, such as hot-wire anemometers.
Dwyer Instruments offers a multitude of sensors for monitoring air velocity in HVAC systems. Some of this instrumentation has a simple construction (Pitot tubes, for example) while others are more complex, such as hot-wire anemometers.