Question: When should I choose a solid state relay over an electromechanical relay?
Answer: In order to best answer this question, we’ll begin with a brief description of each type of relay, followed by a comparison of the two.
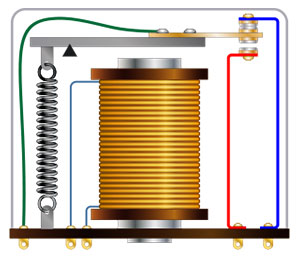
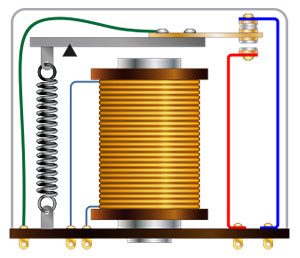
An electromechanical relay uses moving parts that are tied to the contacts of the output to send a control signal. This movement is controlled by electromagnetic forces with low power signals. These power signals allow completion of high power circuitry to connect the load.
The solid state relay will switch using a small external voltage or current signals to the gate of a semiconductor. This means that the switch can change states with no moving parts involved, which will reduce the effects of vibrations and noise on the device. This relay is only available in single pull single throw configurations; but, this can easily be corrected with an intermediate relay.
An electromechanical relay:
- Handles higher current than the solid state version
- Consumes more power, as resistance is a greater factor
- Will be affected by positioning due to gravity and other external forces
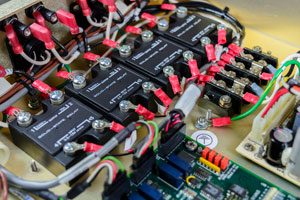
A solid state relay:
- Consumes less power, but generates more heat
- Can be used in virtually any position regardless of the Earth’s pull
- Will be able to respond to control signals about 100 times faster than electromechanical relays (less than 100 micro seconds) while also preventing electrical arcs
- Will have signals less affected by electromagnetic interference
By comparing the benefits of each relay type with your application requirements, you will be able to make an informed decision on which will best suit your needs.