
Dwyer offers several carbon dioxide measuring products that use non-dispersive infrared sensors as the sensing element. Carbon dioxide sensors are commonly used in building automation systems to monitor air quality. The level of carbon dioxide is indirectly proportional to the amount of people in a space and can be used to adjust ventilation for the space.
There are two basic types of gas sensing technologies: chemical reaction and infrared spectroscopic. Most chemical reaction sensors are electrochemical sensors, which are not as reliable as they can interact with multiple gases and wear from interaction with the gas. Continue reading “Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) Carbon Dioxide Sensors”








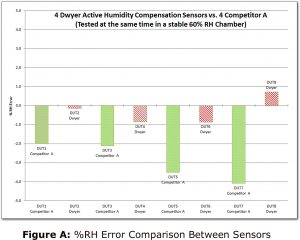 reputation of poor accuracy despite specifications from suppliers. There is a rational reason why these instruments appear to read outside of their stated accuracy, which in turn causes users to be frustrated with the results.
reputation of poor accuracy despite specifications from suppliers. There is a rational reason why these instruments appear to read outside of their stated accuracy, which in turn causes users to be frustrated with the results.